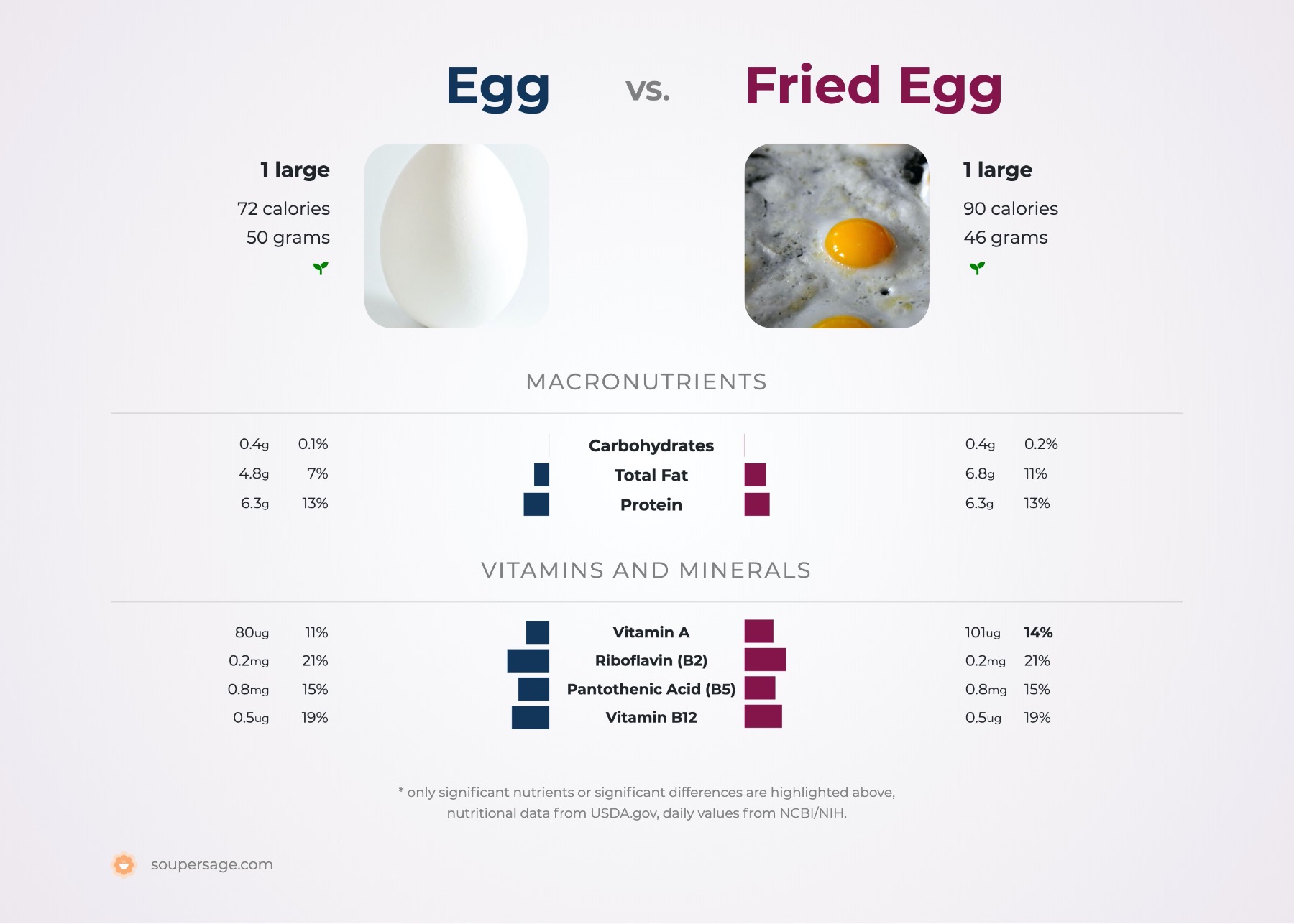
Egg vs. Fried Egg
Nutrition comparison of Egg and Cooked Fried Egg
Ever wonder how your favorite foods stack up against each other in terms of nutrition?
We compared the nutritional contents of
egg
versus
cooked
fried egg
(100g each)
below using 2020 USDA and NIH data[1].
For a quick recap of significant nutrients and differences in egg and fried egg:
- Both egg and fried egg are high in Vitamin A, Vitamin D, calcium, calories, cholesterol and protein.
USDA sources for nutritional information: Egg (Egg, whole, raw, fresh) and Fried Egg (Egg, whole, cooked, fried) . Have a correction or suggestions? Shoot us an email.
Calories and Carbs
calories
Both egg and fried egg are high in calories. Fried egg has 37% more calories than egg - egg has 143 calories per 100 grams and fried egg has 196 calories.
For macronutrient ratios, egg is heavier in protein, lighter in fat and similar to fried egg for carbs. Egg has a macronutrient ratio of 36:2:62 and for fried egg, 29:2:70 for protein, carbohydrates and fat from calories.
Macro Ratios from Calories:
| Egg | Fried Egg | |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 36% | 29% |
| Carbohydrates | 2% | 2% |
| Fat | 62% | 70% |
| Alcohol | ~ | ~ |
carbohydrates
Both egg and fried egg are low in carbohydrates - egg has 0.72g of total carbs per 100 grams and fried egg has 0.83g of carbohydrates.
The carbs in egg and fried egg are both made of 100% sugar.
sugar
Egg and fried egg contain similar amounts of sugar - egg has 0.37g of sugar per 100 grams and fried egg has 0.4g of sugar.
Protein
protein
Both egg and fried egg are high in protein. Egg is very similar to egg for protein - egg has 12.6g of protein per 100 grams and fried egg has 13.6g of protein.
Fat
saturated fat
Egg has 28% less saturated fat than fried egg - egg has 3.1g of saturated fat per 100 grams and fried egg has 4.3g of saturated fat.
trans fat
Both egg and fried egg are low in trans fat - egg has 0.04g of trans fat per 100 grams and fried egg has 0.04g of trans fat.
cholesterol
Both egg and fried egg are high in cholesterol. Egg is very similar to egg for cholesterol - egg has 372mg of cholesterol per 100 grams and fried egg has 401mg of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Vitamin A
Both egg and fried egg are high in Vitamin A. Fried egg has 37% more Vitamin A than egg - egg has 160ug of Vitamin A per 100 grams and fried egg has 219ug of Vitamin A.
Vitamin D
Both egg and fried egg are high in Vitamin D. Egg is very similar to egg for Vitamin D - egg has 82iu of Vitamin D per 100 grams and fried egg has 88iu of Vitamin D.
Vitamin E
Egg and fried egg contain similar amounts of Vitamin E - egg has 1.1mg of Vitamin E per 100 grams and fried egg has 1.3mg of Vitamin E.
Vitamin K
Egg and fried egg contain similar amounts of Vitamin K - egg has 0.3ug of Vitamin K per 100 grams and fried egg has 5.6ug of Vitamin K.
The B Vitamins
Both egg and fried egg contain significant amounts of thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6, folate and Vitamin B12.
| Egg | Fried Egg | |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamin | 0.04 MG | 0.044 MG |
| Riboflavin | 0.457 MG | 0.495 MG |
| Niacin | 0.075 MG | 0.082 MG |
| Pantothenic acid | 1.533 MG | 1.66 MG |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.17 MG | 0.184 MG |
| Folate | 47 UG | 51 UG |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.89 UG | 0.97 UG |
Minerals
calcium
Both egg and fried egg are high in calcium. Egg is very similar to egg for calcium - egg has 56mg of calcium per 100 grams and fried egg has 62mg of calcium.
iron
Egg and fried egg contain similar amounts of iron - egg has 1.8mg of iron per 100 grams and fried egg has 1.9mg of iron.
potassium
Egg and fried egg contain similar amounts of potassium - egg has 138mg of potassium per 100 grams and fried egg has 152mg of potassium.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
carotenoids
Carotenoids are micronutrients commonly found in plants and some animal products. An example is beta-carotene, the notable carotenoid which is a popular source of Vitamin A.[4][5]
For specific types of carotenoids, both egg and fried egg contain significant amounts of lutein + zeaxanthin.
| Egg | Fried Egg | |
|---|---|---|
| lutein + zeaxanthin | 503 UG | 543 UG |
| beta-carotene | ~ | 35 UG |
Omega-3 and Omega-6
omega 3s
For omega-3 fatty acids, fried egg has more alpha linoleic acid (ALA) than egg per 100 grams. Both egg and fried egg contain significant amounts of DHA.
| Egg | Fried Egg | |
|---|---|---|
| alpha linoleic acid | 0.048 G | 0.137 G |
| DHA | 0.058 G | 0.063 G |
| DPA | 0.007 G | 0.007 G |
| Total | 0.113 G | 0.207 G |
omega 6s
Comparing omega-6 fatty acids, both egg and fried egg contain significant amounts of linoleic acid.
| Egg | Fried Egg | |
|---|---|---|
| other omega 6 | 0.018 G | 0.019 G |
| linoleic acid | 1.555 G | 2.781 G |
| Total | 1.573 G | 2.8 G |
Customize your serving size
The comparison below is by weight, but sometimes 100g isn't that intuitive of a measurement for food. View a custom portion comparison (e.g. cups, oz, package).
You can try adding or subtracting the amount of either Egg or Fried Egg .
Egg g
()
|
Daily Values (%) |
Cooked Fried Egg g
()
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCAL % |
|
5% | calories | 5% |
|
KCAL % | |
| G % |
|
5% | carbohydrates | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | dietary fiber | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | sugar | 5% | G | |||
| G % |
|
5% | total fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | saturated fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | monounsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | polyunsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | trans fat | 5% | G | |||
| MG | 5% | cholesterol | 5% | MG | |||
| MG % |
|
5% | sodium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| 5% | Vitamins and Minerals | 5% | |||||
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin A | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin C | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| IU % |
|
5% | Vitamin D | 5% |
|
IU % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | calcium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | iron | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | magnesium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | potassium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | thiamin (Vit B1) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | riboflavin (Vit B2) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | niacin (Vit B3) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B6 | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | pantothenic acid (Vit B5) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | folate (Vit B9) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B12 | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin E | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin K | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| G % |
|
5% | protein | 5% |
|
G % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | biotin (Vit B7) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | choline | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | chlorine | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | chromium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | copper | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | fluoride | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | iodine | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | manganese | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | molybdenum | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | phosphorus | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | selenium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | zinc | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| G | 5% | Water | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Starch | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Alcohol | 5% | G | |||
FAQ
Does egg or fried egg contain more calories in 100 grams?Both egg and fried egg are high in calories. Fried egg has 40% more calories than egg - egg has 143 calories in 100g and fried egg has 196 calories.
Is egg or fried egg better for protein?
Both egg and fried egg are high in protein. Egg is very similar to egg for protein - egg has 12.6g of protein per 100 grams and fried egg has 13.6g of protein.
Does egg or fried egg contain more calcium?
Both egg and fried egg are high in calcium. Egg is very similar to egg for calcium - egg has 56mg of calcium in 100 grams and fried egg has 62mg of calcium.