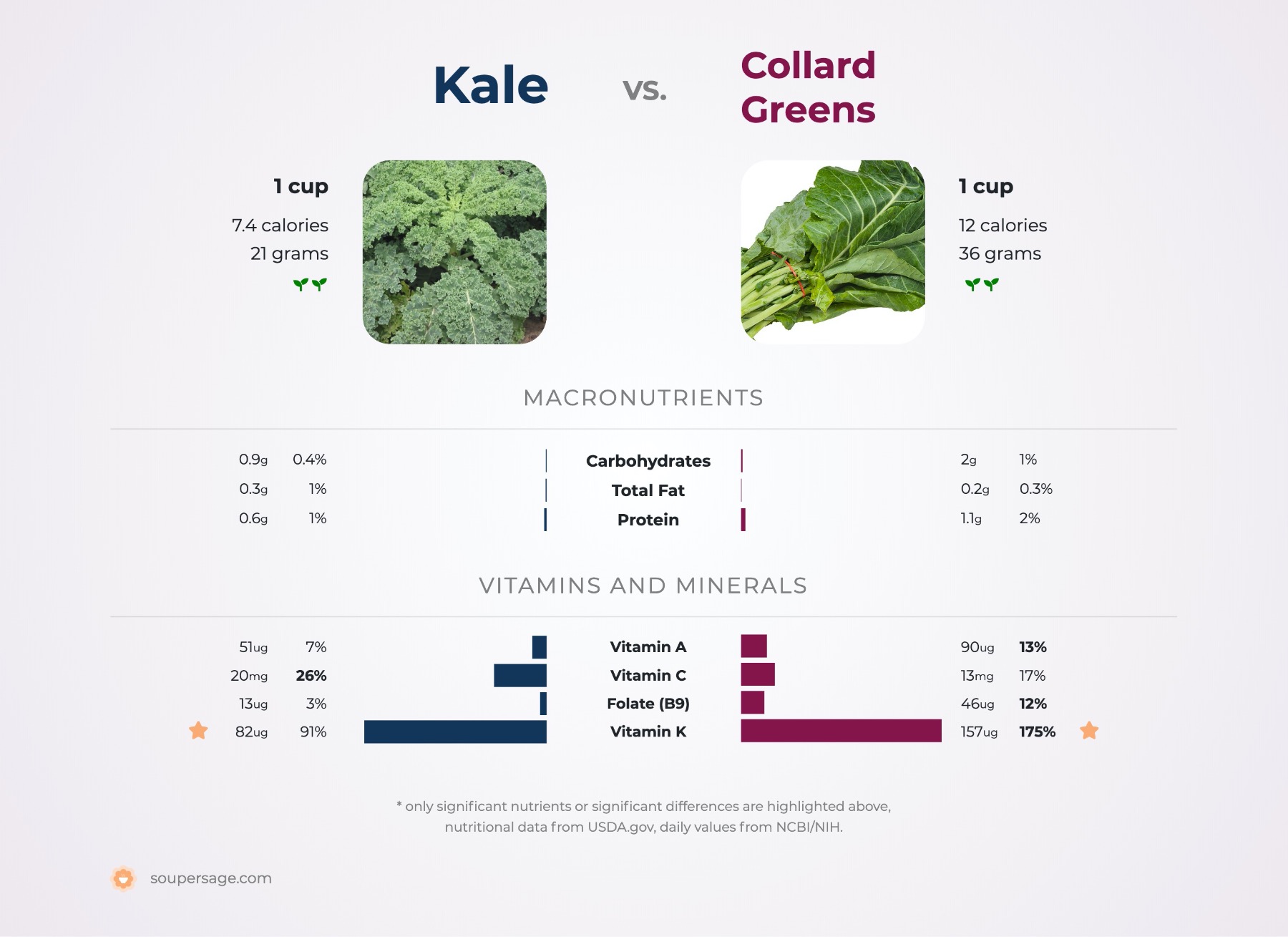
Collard Greens vs. Kale
Nutrition comparison of Collard Greens and Kale
Ever wonder how your favorite foods stack up against each other in terms of nutrition?
We compared the nutritional contents of
collard greens
versus
kale
(100g each)
below using 2020 USDA and NIH data[1].
For a quick recap of significant nutrients and differences in collard greens and kale:
- Both kale and collard greens are high in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin K, calcium, dietary fiber and potassium.
- Kale has more riboflavin.
USDA sources for nutritional information: Collard Greens (Collards, raw) and Kale (Kale, raw) . Have a correction or suggestions? Shoot us an email.
Calories and Carbs
calories
Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of calories - kale has 35 calories per 100 grams and collard green has 32 calories.
For macronutrient ratios, collard greens is heavier in protein, heavier in carbs and lighter in fat compared to kale per calorie. Collard greens has a macronutrient ratio of 31:55:14 and for kale, 27:41:32 for protein, carbohydrates and fat from calories.
Macro Ratios from Calories:
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 31% | 27% |
| Carbohydrates | 55% | 41% |
| Fat | 14% | 32% |
| Alcohol | ~ | ~ |
carbohydrates
Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of carbs - kale has 4.4g of total carbs per 100 grams and collard green has 5.4g of carbohydrates.
The carbs in kale are made of 81% dietary fiber and 19% sugar, whereas the carbs in collard greens comprise of 90% dietary fiber and 10% sugar.
dietary fiber
Both kale and collard greens are high in dietary fiber. Kale is very similar to collard green for dietary fiber - kale has 4.1g of dietary fiber per 100 grams and collard green has 4g of dietary fiber.
sugar
Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of sugar - kale has 0.99g of sugar per 100 grams and collard green has 0.46g of sugar.
Protein
protein
Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of protein - kale has 2.9g of protein per 100 grams and collard green has 3g of protein.
Fat
saturated fat
Both kale and collard greens are low in saturated fat - kale has 0.18g of saturated fat per 100 grams and collard green has 0.06g of saturated fat.
Vitamins
Vitamin C
Both kale and collard greens are high in Vitamin C. Kale has 165% more Vitamin C than collard green - kale has 93.4mg of Vitamin C per 100 grams and collard green has 35.3mg of Vitamin C.
Vitamin A
Both kale and collard greens are high in Vitamin A. Kale is very similar to kale for Vitamin A - kale has 241ug of Vitamin A per 100 grams and collard green has 251ug of Vitamin A.
Vitamin E
Collard green has 242% more Vitamin E than kale - kale has 0.66mg of Vitamin E per 100 grams and collard green has 2.3mg of Vitamin E.
Vitamin K
Both kale and collard greens are high in Vitamin K. Collard green has 12% more Vitamin K than kale - kale has 389.6ug of Vitamin K per 100 grams and collard green has 437.1ug of Vitamin K.
The B Vitamins
Kale has more riboflavin. Both collard greens and kale contain significant amounts of thiamin, niacin, pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6 and folate.
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamin | 0.054 MG | 0.113 MG |
| Riboflavin | 0.13 MG | 0.347 MG |
| Niacin | 0.742 MG | 1.18 MG |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.267 MG | 0.37 MG |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.165 MG | 0.147 MG |
| Folate | 129 UG | 62 UG |
Minerals
calcium
Both kale and collard greens are high in calcium. Kale has a little more calcium (9%) than collard green by weight - kale has 254mg of calcium per 100 grams and collard green has 232mg of calcium.
iron
Kale has 240% more iron than collard green - kale has 1.6mg of iron per 100 grams and collard green has 0.47mg of iron.
potassium
Both kale and collard greens are high in potassium. Kale has 63% more potassium than collard green - kale has 348mg of potassium per 100 grams and collard green has 213mg of potassium.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
flavonoids
Naturally occuring in fruits and vegetables, flavonoids are associated with many health benefits and used in a variety of medicinal and pharmaceutical applications. [2][3]
For specific flavonoid compounds,
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| luteolin | 0.08 mg | ~ |
| kaempferol | 8.74 mg | 46.8 mg |
| Quercetin | 2.57 mg | 22.58 mg |
| isorhamnetin | ~ | 23.6 mg |
carotenoids
Carotenoids are micronutrients commonly found in plants and some animal products. An example is beta-carotene, the notable carotenoid which is a popular source of Vitamin A.[4][5]
For specific types of carotenoids, both collard greens and kale contain significant amounts of beta-carotene and lutein + zeaxanthin.
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| beta-carotene | 2991 UG | 2873 UG |
| alpha-carotene | 14 UG | ~ |
| lutein + zeaxanthin | 4323 UG | 6261 UG |
Omega-3 and Omega-6
omega 3s
For omega-3 fatty acids, kale has more alpha linoleic acid (ALA) than collard green per 100 grams.
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| alpha linoleic acid | 0.108 G | 0.378 G |
| Total | 0.108 G | 0.378 G |
omega 6s
Comparing omega-6 fatty acids, kale has more linoleic acid than collard green per 100 grams.
| Collard Greens | Kale | |
|---|---|---|
| linoleic acid | 0.082 G | 0.291 G |
| other omega 6 | 0.002 G | 0.003 G |
| Total | 0.084 G | 0.294 G |
Customize your serving size
The comparison below is by weight, but sometimes 100g isn't that intuitive of a measurement for food. View a custom portion comparison (e.g. cups, oz, package).
You can try adding or subtracting the amount of either Collard Greens or Kale .
Note: The specific food items compared are: Collard Greens (Collards, raw) and Kale (Kale, raw) .
Collard Greens g
()
|
Daily Values (%) |
Kale g
()
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCAL % |
|
5% | calories | 5% |
|
KCAL % | |
| G % |
|
5% | carbohydrates | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | dietary fiber | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | sugar | 5% | G | |||
| G % |
|
5% | total fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | saturated fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | monounsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | polyunsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | trans fat | 5% | G | |||
| MG | 5% | cholesterol | 5% | MG | |||
| MG % |
|
5% | sodium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| 5% | Vitamins and Minerals | 5% | |||||
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin A | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin C | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| IU % |
|
5% | Vitamin D | 5% |
|
IU % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | calcium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | iron | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | magnesium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | potassium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | thiamin (Vit B1) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | riboflavin (Vit B2) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | niacin (Vit B3) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B6 | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | pantothenic acid (Vit B5) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | folate (Vit B9) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B12 | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin E | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin K | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| G % |
|
5% | protein | 5% |
|
G % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | biotin (Vit B7) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | choline | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | chlorine | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | chromium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | copper | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | fluoride | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | iodine | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | manganese | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | molybdenum | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | phosphorus | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | selenium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | zinc | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| G | 5% | Water | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Starch | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Alcohol | 5% | G | |||
FAQ
Does kale or collard greens contain more calories in 100 grams?Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of calories - kale has 35 calories in 100g and collard green has 32 calories.
Is kale or collard greens better for protein?
Kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of protein - kale has 2.9g of protein per 100 grams and collard green has 3g of protein.
Does kale or collard greens have more carbohydrates?
By weight, kale and collard greens contain similar amounts of carbs - kale has 4.4g of carbs for 100g and collard green has 5.4g of carbohydrates. the carbs in kale are made of 80% dietary fiber and 20% sugar, whereas the carbs in collard greens comprise of 90% dietary fiber and 10% sugar.
Does kale or collard greens contain more calcium?
Both kale and collard greens are high in calcium. Kale has a little more calcium ( 10%) than collard green by weight - kale has 254mg of calcium in 100 grams and collard green has 232mg of calcium.
Does kale or collard greens contain more potassium?
Both kale and collard greens are high in potassium. Kale has 60% more potassium than collard green - kale has 348mg of potassium in 100 grams and collard green has 213mg of potassium.