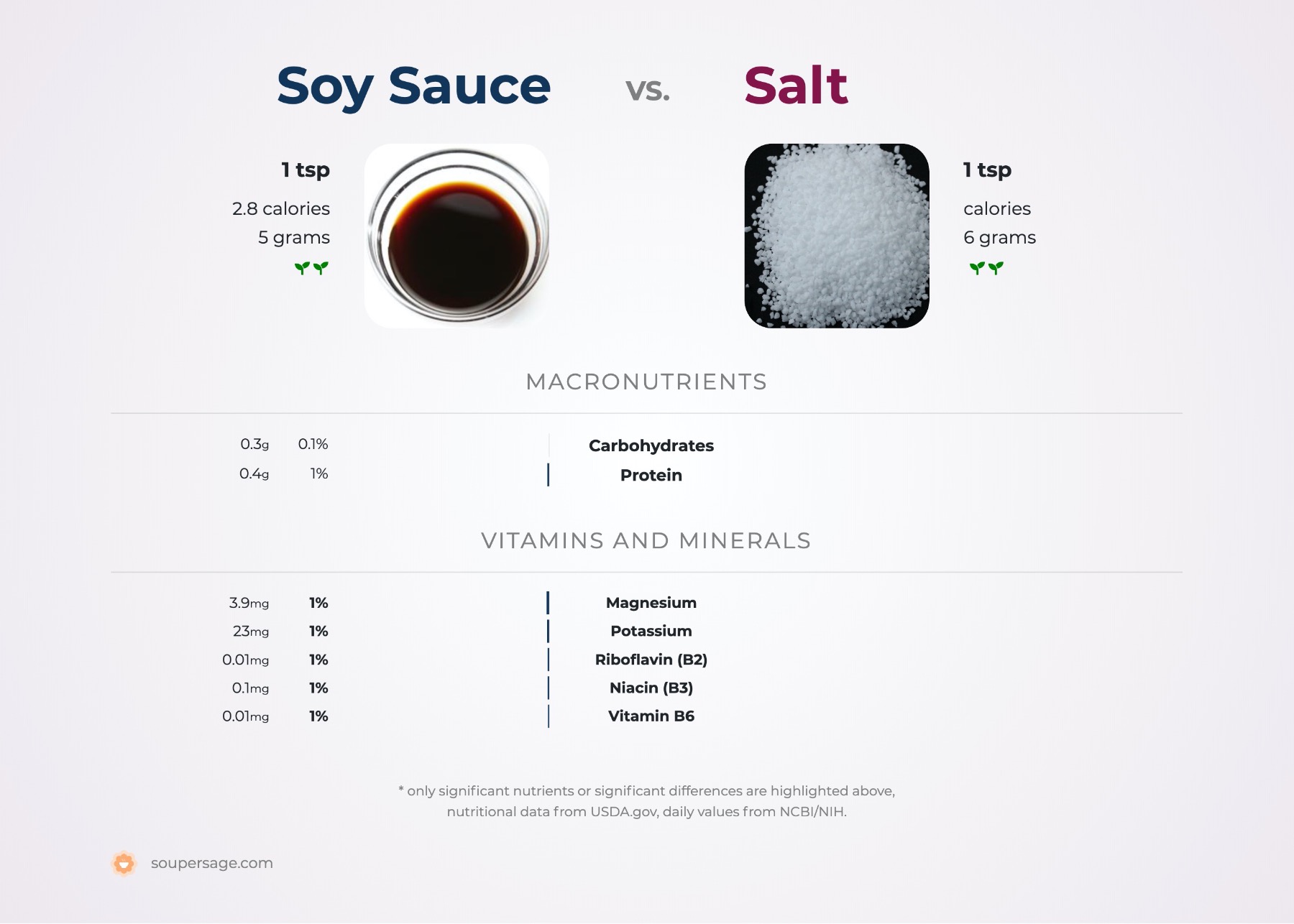
Soy Sauce vs. Salt
Nutrition comparison of Soy Sauce and Salt
Ever wonder how your favorite foods stack up against each other in terms of nutrition?
We compared the nutritional contents of
soy sauce
versus
salt
(100g each)
below using 2020 USDA and NIH data[1].
For a quick recap of significant nutrients and differences in soy sauce and salt:
- Soy sauce has more thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6 and folate.
- Soy sauce is a great source of protein.
- Soy sauce is an excellent source of potassium.
USDA sources for nutritional information: Soy Sauce (Soy sauce made from soy and wheat (shoyu)) and Salt (Salt, table) . Have a correction or suggestions? Shoot us an email.
Calories and Carbs
calories
Salt has less calories than soy sauce - soy sauce has 53 calories per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
| Soy Sauce | Salt | |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 57% | ~ |
| Carbohydrates | 43% | ~ |
| Fat | ~ | ~ |
| Alcohol | ~ | ~ |
carbohydrates
Both soy sauce and salt are low in carbohydrates - soy sauce has 4.9g of total carbs per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
dietary fiber
Soy sauce has more dietary fiber than salt - soy sauce has 0.8g of dietary fiber per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
sugar
Soy sauce and salt contain similar amounts of sugar - soy sauce has 0.4g of sugar per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
Protein
protein
Soy sauce is a great source of protein and it has more protein than salt - soy sauce has 8.1g of protein per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
Fat
saturated fat
Both soy sauce and salt are low in saturated fat - soy sauce has 0.07g of saturated fat per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
Vitamins
The B Vitamins
Soy sauce has more thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6 and folate.
| Soy Sauce | Salt | |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamin | 0.033 MG | ~ |
| Riboflavin | 0.165 MG | ~ |
| Niacin | 2.196 MG | ~ |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.297 MG | ~ |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.148 MG | ~ |
| Folate | 14 UG | ~ |
Minerals
calcium
Soy sauce has 38% more calcium than salt - salt has 24mg of calcium per 100 grams and soy sauce has 33mg of calcium.
iron
Soy sauce has 339% more iron than salt - salt has 0.33mg of iron per 100 grams and soy sauce has 1.5mg of iron.
potassium
Soy sauce is an excellent source of potassium and it has 53 times more potassium than salt - salt has 8mg of potassium per 100 grams and soy sauce has 435mg of potassium.
Customize your serving size
The comparison below is by common portions, e.g. cups, packages. You can also see a more concrete comparison by weight at equal weight (by grams) comparison.
Soy Sauce g
()
|
Daily Values (%) |
Salt g
()
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCAL % |
|
5% | calories | 5% |
|
KCAL % | |
| G % |
|
5% | carbohydrates | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | dietary fiber | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | sugar | 5% | G | |||
| G % |
|
5% | total fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | saturated fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | monounsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | polyunsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | trans fat | 5% | G | |||
| MG | 5% | cholesterol | 5% | MG | |||
| MG % |
|
5% | sodium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| 5% | Vitamins and Minerals | 5% | |||||
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin A | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin C | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| IU % |
|
5% | Vitamin D | 5% |
|
IU % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | calcium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | iron | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | magnesium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | potassium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | thiamin (Vit B1) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | riboflavin (Vit B2) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | niacin (Vit B3) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B6 | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | pantothenic acid (Vit B5) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | folate (Vit B9) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B12 | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin E | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin K | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| G % |
|
5% | protein | 5% |
|
G % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | biotin (Vit B7) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | choline | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | chlorine | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | chromium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | copper | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | fluoride | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | iodine | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | manganese | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | molybdenum | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | phosphorus | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | selenium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | zinc | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| G | 5% | Water | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Starch | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Alcohol | 5% | G | |||
FAQ
Does soy sauce or salt contain more calories in 100 grams?Salt has less calories than soy sauce - soy sauce has 53 calories in 100g and salt does not contain significant amounts.
Is soy sauce or salt better for protein?
Soy sauce is a great source of protein and it has more protein than salt - soy sauce has 8.1g of protein per 100 grams and salt does not contain significant amounts.
Does soy sauce or salt have more carbohydrates?
By weight, both soy sauce and salt are low in carbohydrates - soy sauce has 4.9g of carbs for 100g and salt has no carbs..
Does salt or soy sauce contain more potassium?
Soy sauce is a rich source of potassium and it has 53 times more potassium than salt - salt has 8mg of potassium in 100 grams and soy sauce has 435mg of potassium.