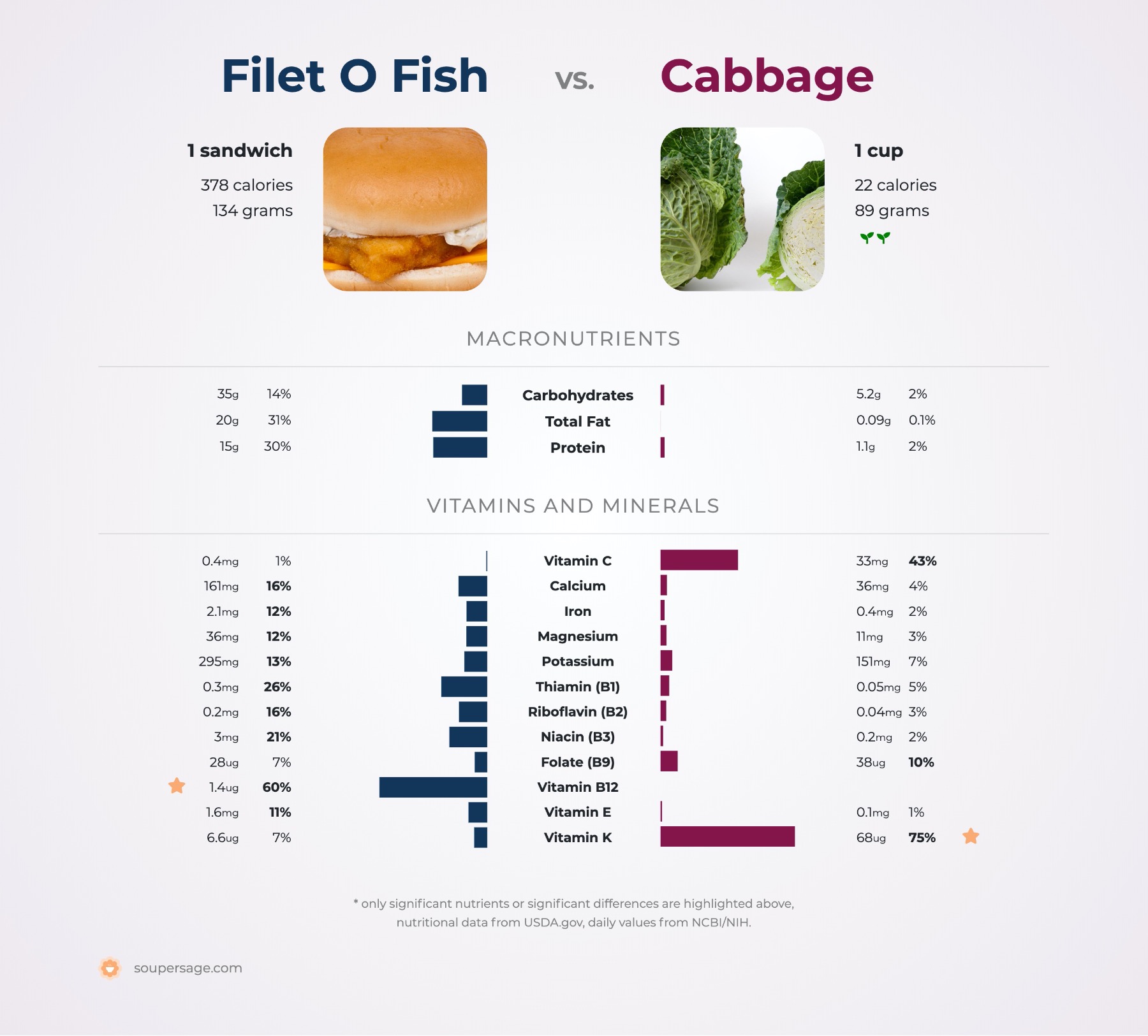
Filet O Fish vs. Cabbage
Nutrition comparison of Filet O Fish and Cabbage
Ever wonder how your favorite foods stack up against each other in terms of nutrition?
We compared the nutritional contents of
filet o fish
versus
cabbage
(100g each)
below using 2020 USDA and NIH data[1].
For a quick recap of significant nutrients and differences in filet o fish and cabbage:
- Cabbage has 3.5 times less carbohydrates than filet o fish.
- Cabbage has 82.3 times less saturated fat than filet o fish.
- Cabbage has signficantly more Vitamin K than filet o fish.
- Cabbage is a great source of dietary fiber.
- Cabbage is an excellent source of Vitamin C.
- Filet o fish has more thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and Vitamin B12, however, cabbage contains more pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6 and folate.
- Filet o fish is a great source of potassium and protein.
- Filet o fish is an excellent source of calcium.
USDA sources for nutritional information: Filet O Fish (McDONALD'S, FILET-O-FISH) and Cabbage (Cabbage, raw) . Have a correction or suggestions? Shoot us an email.
Calories and Carbs
calories
Filet o fish is high in calories and cabbage has 91% less calories than filet o fish - cabbage has 25 calories per 100 grams and filet o fish has 282 calories.
For macronutrient ratios, filet o fish is much lighter in carbs, much heavier in fat and similar to cabbage for protein. Filet o fish has a macronutrient ratio of 16:37:47 and for cabbage, 17:80:3 for protein, carbohydrates and fat from calories.
Macro Ratios from Calories:
| Filet O Fish | Cabbage | |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 16% | 17% |
| Carbohydrates | 37% | 80% |
| Fat | 47% | 3% |
| Alcohol | ~ | ~ |
carbohydrates
Cabbage has 3.5 times less carbohydrates than filet o fish - cabbage has 5.8g of total carbs per 100 grams and filet o fish has 26.4g of carbohydrates.
dietary fiber
Cabbage is a great source of dietary fiber and it has 79% more dietary fiber than filet o fish - cabbage has 2.5g of dietary fiber per 100 grams and filet o fish has 1.4g of dietary fiber.
sugar
Cabbage and filet o fish contain similar amounts of sugar - cabbage has 3.2g of sugar per 100 grams and filet o fish has 3.7g of sugar.
Protein
protein
Filet o fish is a great source of protein and it has 780% more protein than cabbage - cabbage has 1.3g of protein per 100 grams and filet o fish has 11.3g of protein.
Fat
saturated fat
Cabbage has 82.3 times less saturated fat than filet o fish - cabbage has 0.03g of saturated fat per 100 grams and filet o fish has 2.8g of saturated fat.
trans fat
Both filet o fish and cabbage are low in trans fat - filet o fish has 0.13g of trans fat per 100 grams and cabbage does not contain significant amounts.
cholesterol
Cabbage has less cholesterol than filet o fish - filet o fish has 32mg of cholesterol per 100 grams and cabbage does not contain significant amounts.
Vitamins
Vitamin C
Cabbage is an excellent source of Vitamin C and it has 121 times more Vitamin C than filet o fish - cabbage has 36.6mg of Vitamin C per 100 grams and filet o fish has 0.3mg of Vitamin C.
Vitamin A
Cabbage and filet o fish contain similar amounts of Vitamin A - cabbage has 5ug of Vitamin A per 100 grams and filet o fish does not contain significant amounts.
Vitamin E
Cabbage and filet o fish contain similar amounts of Vitamin E - cabbage has 0.15mg of Vitamin E per 100 grams and filet o fish has 1.2mg of Vitamin E.
Vitamin K
Cabbage has signficantly more Vitamin K than filet o fish - cabbage has 76ug of Vitamin K per 100 grams and filet o fish has 4.9ug of Vitamin K.
The B Vitamins
Filet o fish has more thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and Vitamin B12, however, cabbage contains more pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6 and folate.
| Filet O Fish | Cabbage | |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamin | 0.211 MG | 0.061 MG |
| Riboflavin | 0.13 MG | 0.04 MG |
| Niacin | 2.22 MG | 0.234 MG |
| Pantothenic acid | ~ | 0.212 MG |
| Vitamin B6 | ~ | 0.124 MG |
| Folate | 21 UG | 43 UG |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.08 UG | ~ |
Minerals
calcium
Filet o fish is an excellent source of calcium and it has 200% more calcium than cabbage - cabbage has 40mg of calcium per 100 grams and filet o fish has 120mg of calcium.
iron
Filet o fish has 232% more iron than cabbage - cabbage has 0.47mg of iron per 100 grams and filet o fish has 1.6mg of iron.
potassium
Filet o fish is a great source of potassium and it has 29% more potassium than cabbage - cabbage has 170mg of potassium per 100 grams and filet o fish has 220mg of potassium.
Omega-3 and Omega-6
omega 6s
Comparing omega-6 fatty acids, filet o fish has more linoleic acid than cabbage per 100 grams.
| Filet O Fish | Cabbage | |
|---|---|---|
| other omega 6 | 0.006 G | ~ |
| linoleic acid | 5.187 G | 0.017 G |
| Total | 5.193 G | 0.017 G |
Customize your serving size
The comparison below is by common portions, e.g. cups, packages. You can also see a more concrete comparison by weight at equal weight (by grams) comparison.
Note: The specific food items compared are: Filet O Fish (McDONALD'S, FILET-O-FISH) and Cabbage (Cabbage, raw) .
Filet O Fish g
()
|
Daily Values (%) |
Cabbage g
()
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCAL % |
|
5% | calories | 5% |
|
KCAL % | |
| G % |
|
5% | carbohydrates | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | dietary fiber | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | sugar | 5% | G | |||
| G % |
|
5% | total fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G % |
|
5% | saturated fat | 5% |
|
G % | |
| G | 5% | monounsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | polyunsaturated fat | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | trans fat | 5% | G | |||
| MG | 5% | cholesterol | 5% | MG | |||
| MG % |
|
5% | sodium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| 5% | Vitamins and Minerals | 5% | |||||
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin A | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin C | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| IU % |
|
5% | Vitamin D | 5% |
|
IU % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | calcium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | iron | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | magnesium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | potassium | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | thiamin (Vit B1) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | riboflavin (Vit B2) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | niacin (Vit B3) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B6 | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | pantothenic acid (Vit B5) | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | folate (Vit B9) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin B12 | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | Vitamin E | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | Vitamin K | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| G % |
|
5% | protein | 5% |
|
G % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | biotin (Vit B7) | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | choline | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | chlorine | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | chromium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | copper | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | fluoride | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | iodine | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | manganese | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | molybdenum | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | phosphorus | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| UG % |
|
5% | selenium | 5% |
|
UG % | |
| MG % |
|
5% | zinc | 5% |
|
MG % | |
| G | 5% | Water | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Starch | 5% | G | |||
| G | 5% | Alcohol | 5% | G | |||
FAQ
Does cabbage or filet o fish contain more calories in 100 grams?Filet o fish is high in calories and cabbage has 90% less calories than filet o fish - cabbage has 25 calories in 100g and filet o fish has 282 calories.
Does cabbage or filet o fish have more carbohydrates?
By weight, cabbage has 3.5 times fewer carbohydrates than filet o fish - cabbage has 5.8g of carbs for 100g and filet o fish has 26.4g of carbohydrates.
Does cabbage or filet o fish contain more calcium?
Filet o fish is a rich source of calcium and it has 200% more calcium than cabbage - cabbage has 40mg of calcium in 100 grams and filet o fish has 120mg of calcium.